Query Filters
1. Usage
SELECT action AS "action::filter", COUNT(0) AS "actions count"
FROM events
GROUP BY action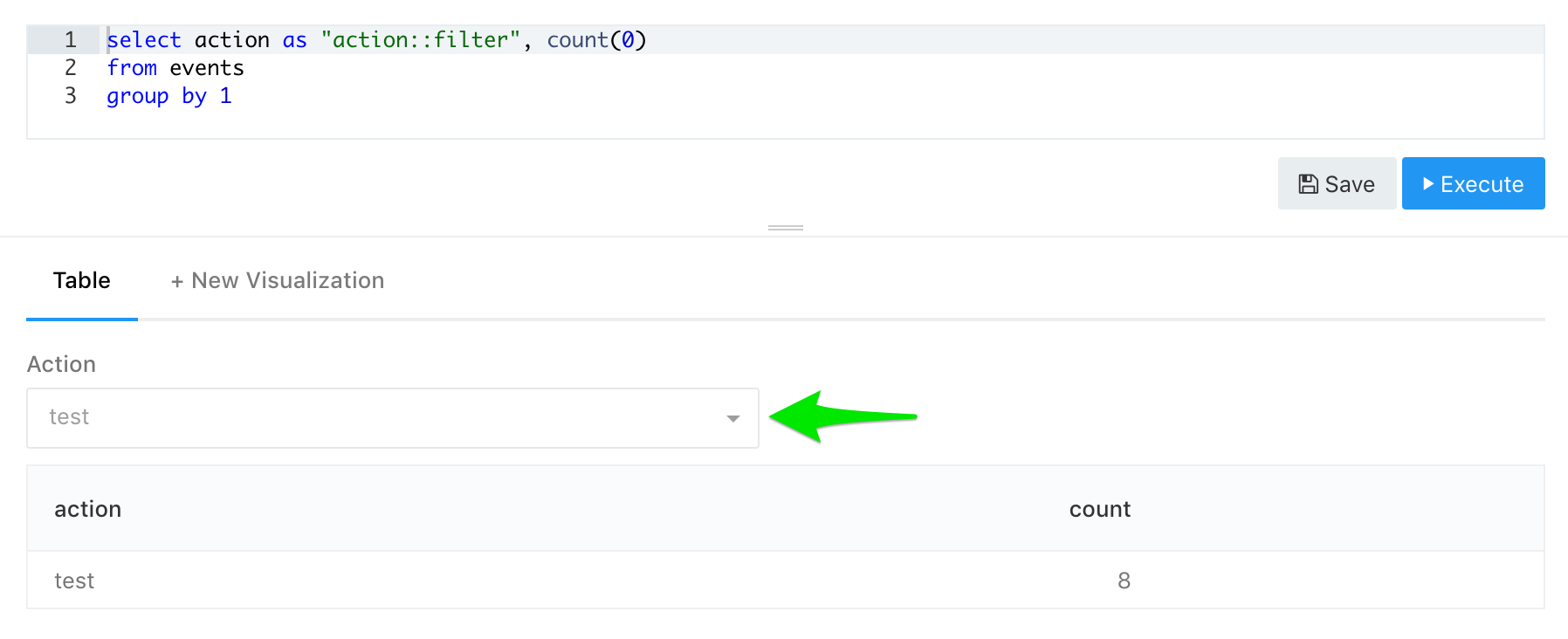
2. Limitations
Last updated
Was this helpful?
SELECT action AS "action::filter", COUNT(0) AS "actions count"
FROM events
GROUP BY action

Last updated
Was this helpful?
Was this helpful?
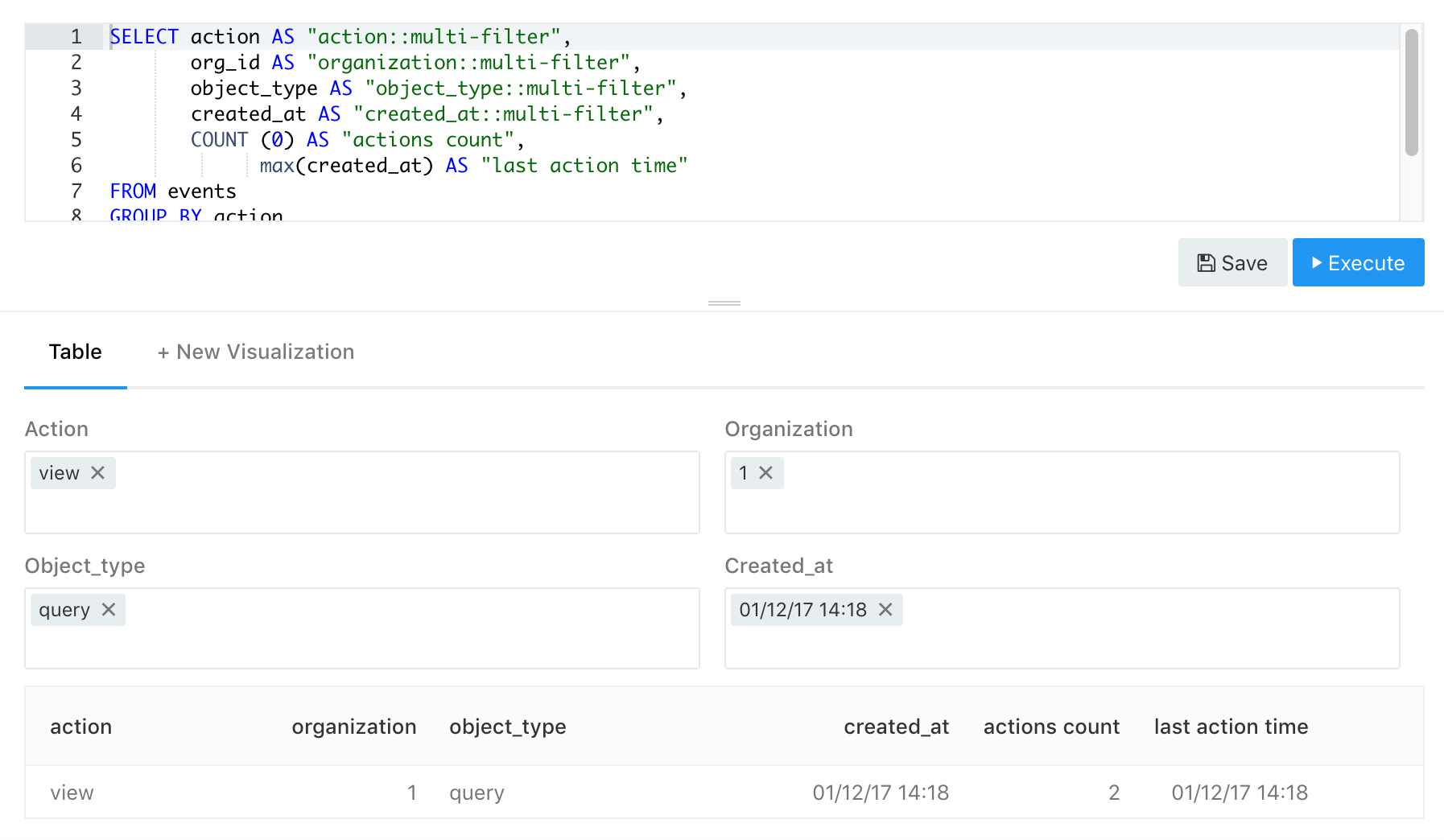
SELECT action AS "action::multi-filter", COUNT (0) AS "actions count"
FROM events
GROUP BY action